In this Linux Ubuntu tutorial, we explain how to kill a process or Program in Linux Ubuntu. There are a number of reasons why you would like to terminate a process. Namely, sometimes even if you close an application, the background processes of the same application will still run. On the other hand, sometimes an application might become unresponsive and you would need to terminate it manually. The YouTube video accompanying this tutorial is given below.
There are several ways to kill or terminate a process or an application in Linux Ubuntu.
1. Kill the process on the basis of its PID
In Linux systems, the Process IDentification, or briefly PID is a unique identifier and number assigned to each process or a subprocess of an application running on a Linux System. On the other hand, we also have a PPID number. A PPID stands for Parent Process IDentification. This is the process that created the PID process.
First, let us find the PID identification of the process or program. To do that open a terminal and type:
ps -efThis will list the currently running processes and programs in Linux Ubuntu. You should see an output similar to this:
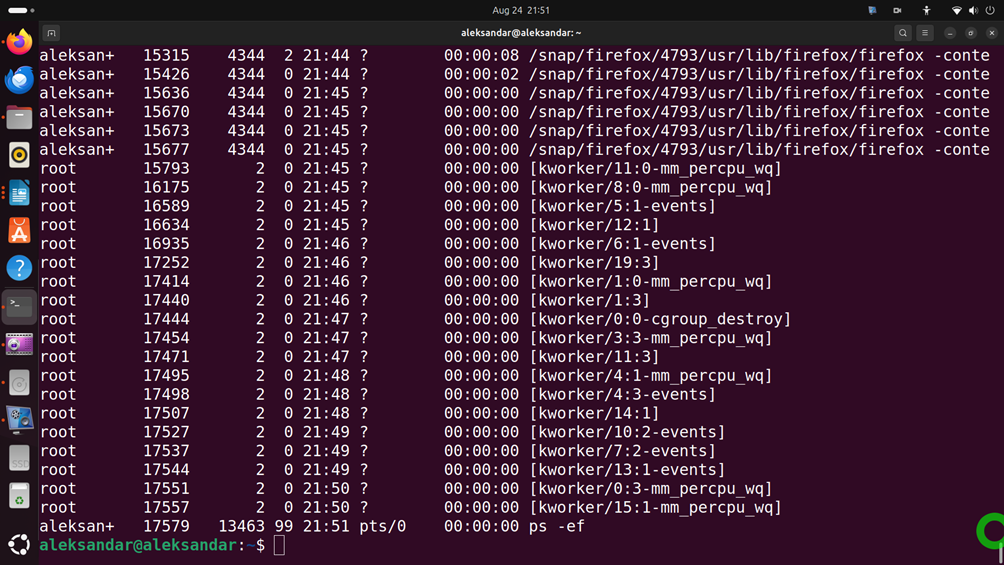
The second column represents the PID of the process.
You can also type
ps auxto get a more detailed response including CPU and memory usage:
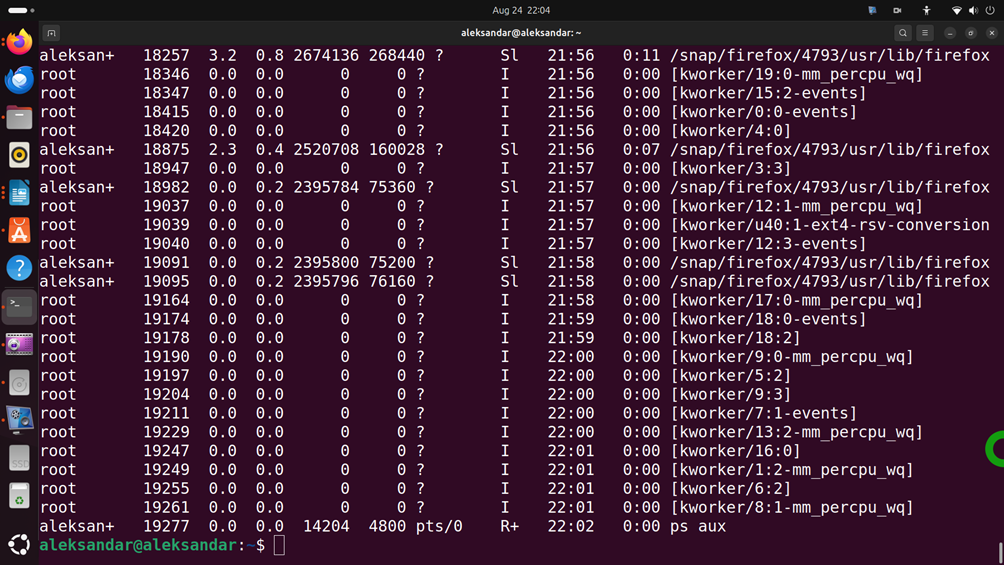
Now, you need to identify the process that you want to terminate. That is, you need to find its PID. You can either search the list or you can filter the results by typing this:
ps -ef | grep <name of the process>For example, if I want to find a process called snapshot. I will simply type
ps -ef | grep snapshotThe result will look like this
aleksan+ 19605 2916 3 22:08 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/snapshotWe can also find the PID of a process by using the command
pidof <process name>For example, to find the PID of firefox, we will simply type
pidof firefoxThe output will look like this
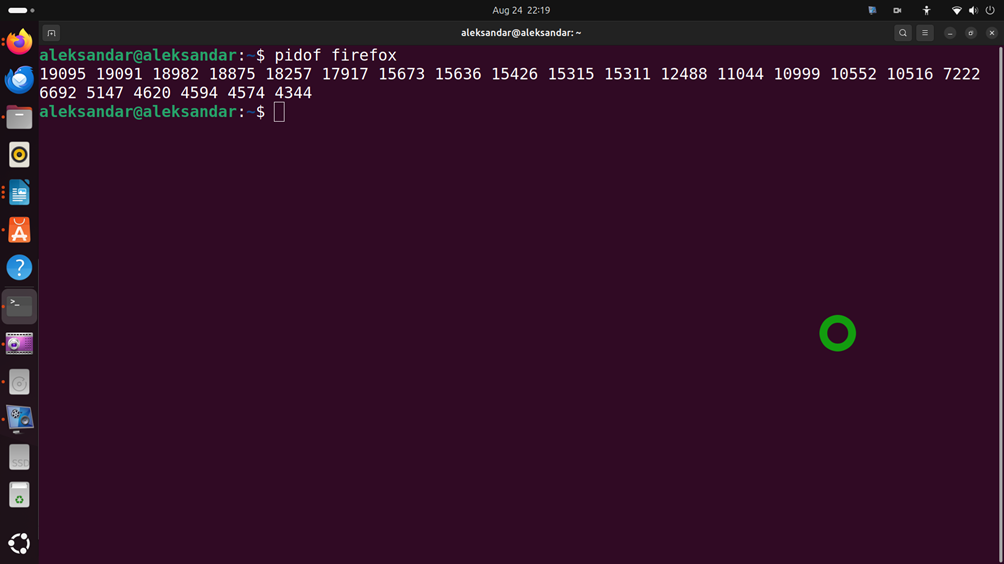
We can see that there are several processes associated with firefox apps.
To modify the execution of a specific process, we need to use the kill command. To kill this process, we will need to type
kill <signal> <PID>This will send a kill signal to that process that will terminate the process with the specific PID. For example, to kill the process/app called snapshot, we need to write this:
kill -9 19605The command kill has other options also:
SIGHUP -1 Hangup
SIGINT -2 Interrupt from keyboard
SIGKILL -9 Kill signal
SIGTERM -15 Termination signal- allow the program to run the exit code and stop its processing
SIGSTOP -17, -19, -23 Stop the process
2. Kill the process on the basis of its Name
To kill the process/application on the basis of its name, we simply need to write
killall <application or process name>For example, if we want to kill firefox, we will simply write
kilall firefoxAnother approach is to use the command pkill
Again, we will simply write
pkill <name of the process or application>