In this tutorial, we explain how to install ROS2 Humble Hawksbill in Ubuntu 22.04. In our next tutorial, we explain how to install ROS2 Humble Hawksbill in Ubuntu 20.04. Furthermore, we explain how to properly verify the installation by running a talker-listener ROS2 example. This example can be seen as a Hello World program of ROS2 programming. The YouTube video accompanying this tutorial is given below.
STEP 1: Verify that you have the correct version of Linux and make sure that other versions of ROS1/ROS2 are NOT automatically sourced in the .bashrc file.
First, verify that you have the correct version of the Linux operating system. Open a terminal, and in the terminal type:
cat /etc/os-releaseYou should see this:
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION_ID="22.04"
VERSION="22.04.3 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish)"
VERSION_CODENAME=jammy
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/"
PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy"
UBUNTU_CODENAME=jammy
If you see Ubuntu 22.04 (the third number does not matter), this means that you have the proper version of Linux.
Next, we need to make sure that some other versions of ROS2 or even ROS1 are not automatically sourced when you start a terminal. Namely, you can have several ROS2 distributions installed on your system, however, they should not be sourced when you start a terminal. Sourced means that a setup file of a ROS2 distribution is automatically called when you open a terminal. The first check is to type this:
printenv ROS_DISTROIf you do not see any output, this means that other ROS2 installations are not sourced. This is what we want. On the other hand, if you see some output, such as “iron” for example, this means that “iron” ROS2 distribution is automatically sourced when a terminal is opened. The next check is to inspect the file called “.bashrc”. This is a setup file that is automatically executed when a terminal is opened. Type
sudo apt-get install gedit
cd ~
gedit .bashrc
Nowhere in the file, you should see a line that looks like this
source /opt/ros/iron/setup.bashwhere “iron” is the Iron ROS2 distributions. Similarly, you should not see any source command for any setup.bash file of any ROS1 or ROS2 distributions. If you see such a line, simply erase the line.
STEP 2: Configure your Ubuntu repositories to allow “restricted,” “universe,” and “multiverse.”
Open a new terminal, and type:
sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo add-apt-repository multiverse
sudo add-apt-repository restricted
sudo apt install software-properties-common
To verify, type this:
grep ^deb /etc/apt/sources.listSTEP 3: Set locale and setup resources
We need to have a locale that supports UTF-8. Let us do this to ensure that this is the case
locale
sudo apt update && sudo apt install locales
sudo locale-gen en_US en_US.UTF-8
sudo update-locale LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 LANG=en_US.UTF-8
export LANG=en_US.UTF-8
locale
Now add the ROS 2 GPG key with apt.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install curl -y
sudo curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ros/rosdistro/master/ros.key -o /usr/share/keyrings/ros-archive-keyring.gpg
Let us add the repository to the source list
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/ros-archive-keyring.gpg] http://packages.ros.org/ros2/ubuntu $(. /etc/os-release && echo $UBUNTU_CODENAME) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros2.list > /dev/nullSTEP 4: Install ROS2 packages
Update the caches and the system:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Install ROS2 Humble
sudo apt install ros-humble-desktop
sudo apt install ros-dev-tools
STEP 5: Test the installation by running the talker-listener example
The talker-listener example is a “Hello World” example of ROS2 programming. It is often used to verify the ROS2 installation. Open a new terminal, and in that new terminal first source the ROS2 environment and after that run the talker node
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker
You will see the talker messages in the terminal window:
[INFO] [1710400774.890608184] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 1'
[INFO] [1710400775.890613598] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 2'
[INFO] [1710400776.890617921] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 3'
[INFO] [1710400777.890611464] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 4'
[INFO] [1710400778.890635038] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 5'
[INFO] [1710400779.890634112] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 6'
[INFO] [1710400780.890644541] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 7'
[INFO] [1710400781.890599980] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 8'
[INFO] [1710400782.890681589] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 9'
[INFO] [1710400783.890693583] [talker]: Publishing: 'Hello World: 10'Remember, every time you want to do something in ROS2, you need to source the file called “setup.bash”. Then, while the first terminal is opened, open a new terminal, and source the environment and run the listener node:
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run demo_nodes_py listener
Then you will see the listener messages in your terminal window.
[INFO] [1710400778.926790079] [listener]: I heard: [Hello World: 5]
[INFO] [1710400779.892853565] [listener]: I heard: [Hello World: 6]
[INFO] [1710400780.892894611] [listener]: I heard: [Hello World: 7]
[INFO] [1710400781.892771878] [listener]: I heard: [Hello World: 8]
[INFO] [1710400782.892902394] [listener]: I heard: [Hello World: 9]
[INFO] [1710400783.893113481] [listener]: I heard: [Hello World: 10]
To see a list of all available topics, open a new terminal, and type
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 topic list
As the output, you will see
/chatter
/parameter_events
/rosout
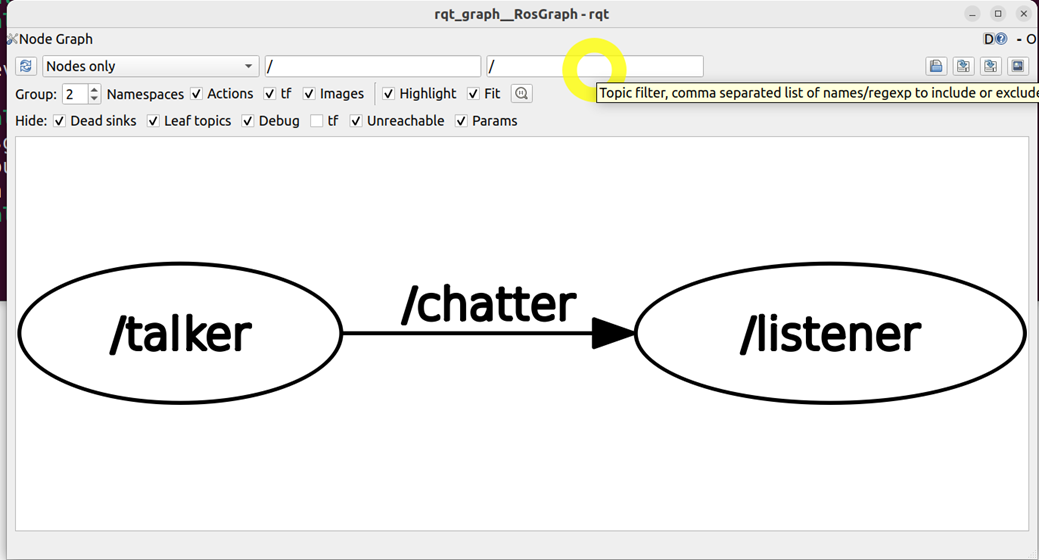
The node called “talker” sends string messages to the node called “listener”. The listener node displays the messages in the terminal window.
Then, to obtain more information about a specific topic, type
ros2 topic info /chatterYou will see that the messages are of the type “std_msgs/msg/String”. This is a ROS2 data type that is equivalent to the string data type in Python and C++
Another important command is
rqt_graphThis command will bring up a graph describing the topic-node structure of our ROS2 system. The graph is given below.