In this Linux tutorial for robotics, robot operating system, control, and machine learning, we explain how to copy, move, rename, and delete files and folders in Linux Ubuntu. The YouTube tutorial is given below.
Create and Erase Folders and Files in Linux Ubuntu
First of all, open a new terminal, and type
cd ~To navigate to the home folder. The tilde “~” symbol in Linux Ubuntu is the symbol for the home folder. To create a new directory (folder) called “dir1”, use the command mkdir
mkdir dir1We can create several directories at the same time, by using the option -p with the command mkdir
mkdir -p dir2/sub_dir1This command will create a parent directory called “dir2” and inside it will create a child directory called “sub_dir1”. To navigate to the newly created folder, we need to type
cd dir1To go back to the parent folder, we need to type
cd .. To navigate directly to the folder sub_dir1, we need to type the absolute path
cd ~/dir2/sub_dir1To go back to the home folder, we can type
cd ~To erase the folder and all the subfolders, we need to type
rm -r ~/dir2However, sometimes it is a good idea to use rm with an additional option -v. This option will print what has been erased. The option -v stands for verbose. Let us illustrate this by creating folders and by erasing them
mkdir -p ~/dir2/dir2_subLet us create an empty file in the folder dir2
touch ~/dir2/file2 Let us list the content of the folder dir2
ls -la ~/dir2total 12
drwxr-xr-x 3 ahaber ahaber 4096 Oct 31 12:11 .
drwxr-x--- 18 ahaber ahaber 4096 Oct 31 12:11 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 ahaber ahaber 4096 Oct 31 12:11 dir2_sub
-rw-r--r-- 1 ahaber ahaber 0 Oct 31 12:11 file2
Then, let us erase with the option -rv
rm -rv dir2The output while erasing is now verbose:
removed 'dir2/file2'
removed directory 'dir2/dir2_sub'
removed directory 'dir2
Next, we explain how to create and erase files. Let us create and navigate to a new folder:
mkdir ~/dir10
cd ~/dir10
We can easily create an empty file by using the command touch:
touch file1Let us add some text to this file by using the echo command and the redirection operator “>”
echo First line of the file > file1To show the content of the file, simply type
cat file1 If we again use the command echo with the redirected output, the content of the file will be erased and a new line will be written. To see this, type this
echo New line > file1
cat file1We can see that the content of the file has been erased. Let us now explain how to append the content of the file by using the echo command. First let us again add the first line
echo First line of the file > file1Then, to append the content of the file, we need to use the operator “>>”. To append the file, type this
echo Second line of the file >> file1To show the content of the file, simply type
cat file1 you will get these two lines as the output:
First line of the file
Second line of the file
To erase a single file, we can use several commands. Usually, I use the command rm
rm file1To erase several files, let us first create them. Let us create three files. We can do that by using a single touch command
touch file2 file3 file4To erase these files, type
rm *Where the star symbol “*” (asterisk) means that we want to erase all the files in the current folder. If you again type
ls -laYou will see that the folder is empty. However, the operator * will not erase the hidden files. In Linux, the hidden files start with a period (dot symbol) “.”. That is, you can identify the hidden files simply by checking if they start with a dot symbol. To explain how to erase both normal and hidden files let us create a mix of normal and hidden files. To do that type
touch file1 .file2 file3 .file4Let us list the content of the current folder:
ls -laType now
rm *
ls -la
You will get
drwxr-xr-x 2 ahaber ahaber 4096 Oct 31 12:26 .
drwxr-x--- 17 ahaber ahaber 4096 Oct 31 12:12 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 ahaber ahaber 0 Oct 31 12:25 .file2
-rw-r--r-- 1 ahaber ahaber 0 Oct 31 12:25 .file4
This means that only the files that are not hidden are erased. Let us create again the files
touch file1 file3
ls -la
Then, to erase all files, including the hidden files, we need to type this
rm -v {*,.*}Let us now erase all the created files and folders
cd ~
rm -r ~/dir10
rm -r ~/dir1Copy, Move, and Rename Files and Folders in Linux Ubuntu
Next, we explain how to copy, move, and rename files and folders. In the Linux and Unix worlds, moving and renaming files and folders are the same thing. To rename the file, let us create a new folder in the home folder and let us navigate to this new folder:
cd ~
mkdir dir3
cd dir3
Let us create a new file and let us add a content to that file:
touch file2
echo New Line > file2
Let us rename the file. To rename file2 as file3, we need to type
mv file2 file3The first input parameter is the name of the original file, and the second input parameter is the new name.
Let us make sure that the file is renamed
ls -la
cat file3
Next, we explain how to move the file from one folder to another. Let us create a new folder in the home folder called dir4. In the current folder, we can type
mkdir ~/dir4Where we specified the absolute path of the new folder. To move the file to the new folder, we need to type
mv file3 ~/dir4The first input parameter is the name of the file we want to move and the second input parameter is the path of the destination folder.
Let us now make sure that the file is moved. In the current folder type
ls -la and you will see that the file does not exist. Then, type
ls -la ~/dir4to list the content of the folder dir4. The content is
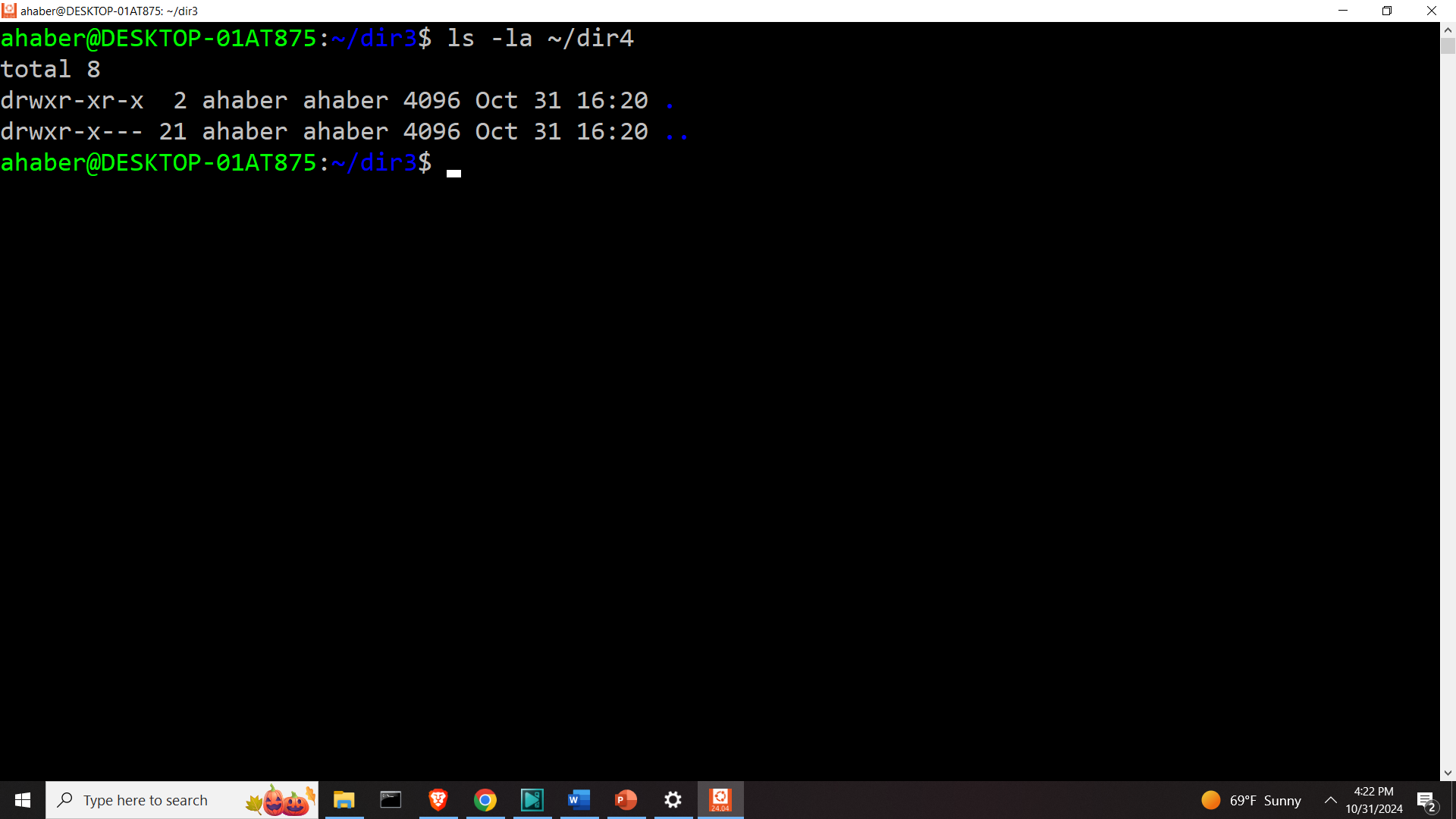
Next, let us erase the two folders
cd ~
rm -r ~/dir3
rm -r ~/dir4Let us learn how to move one folder to another. To do that, let us go to the home folder and create two folders
cd ~
mkdir folder1
mkdir folder2
Let us create files in folder1:
touch ~/folder1/file1.txt ~/folder1/file2.txtLet us list the content
ls -la ~/folder1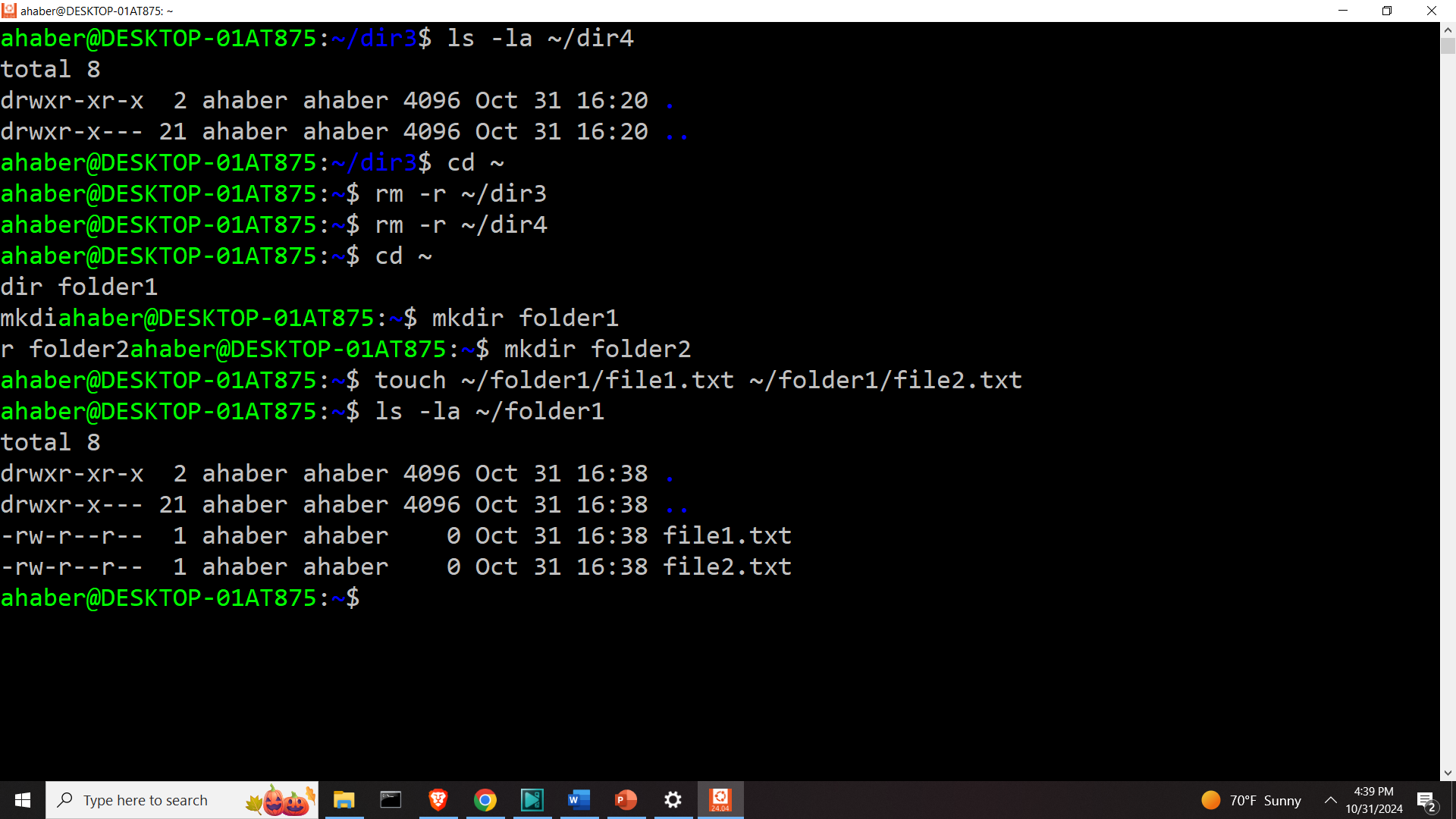
Let us move the folder folder1 to folder2
mv ~/folder1 ~/folder2Let us list the content of the folder2
ls -la ~/folder2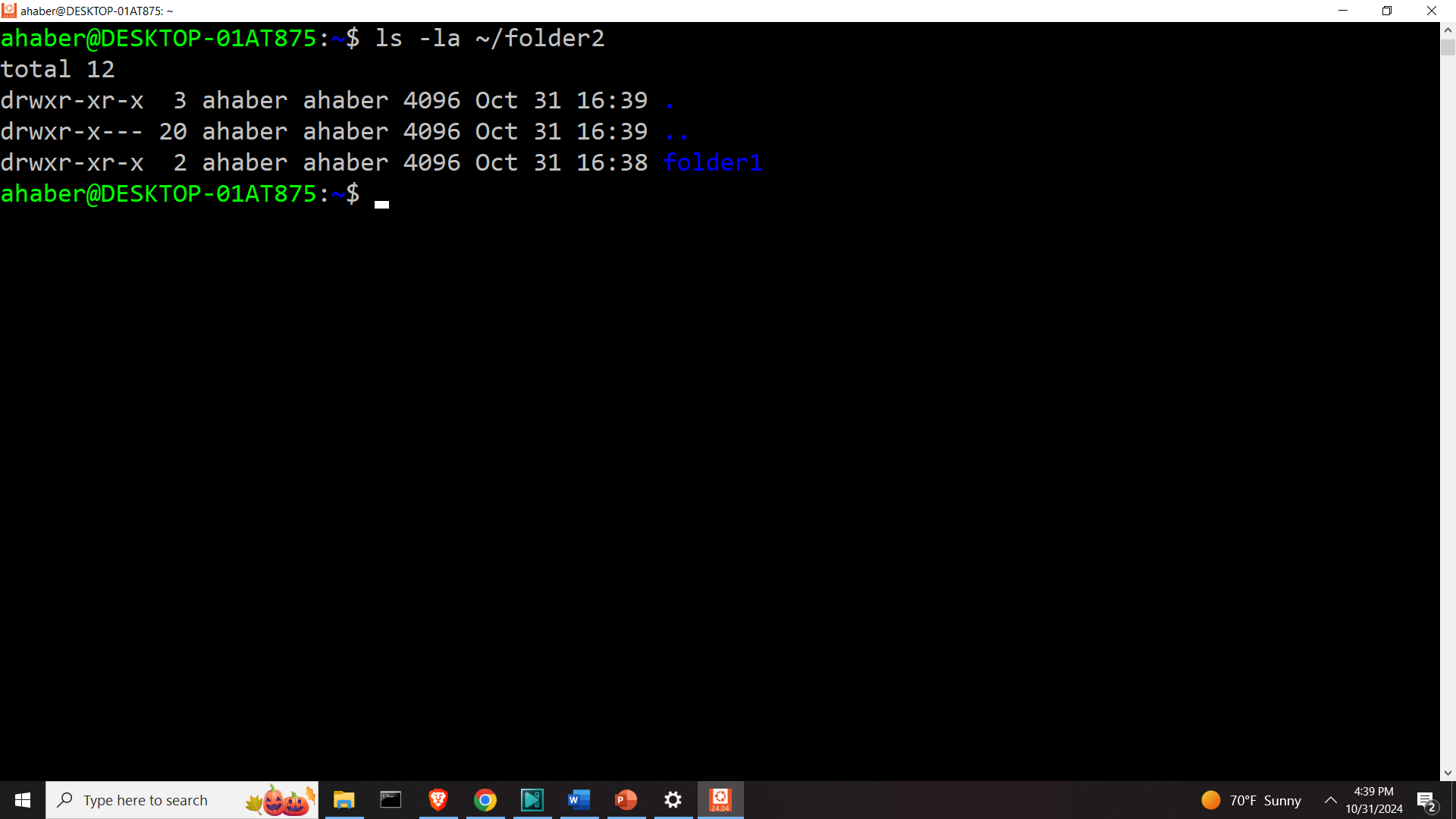
Let us list the content of the folder1 inside of the folder2
ls -la ~/folder2/folder1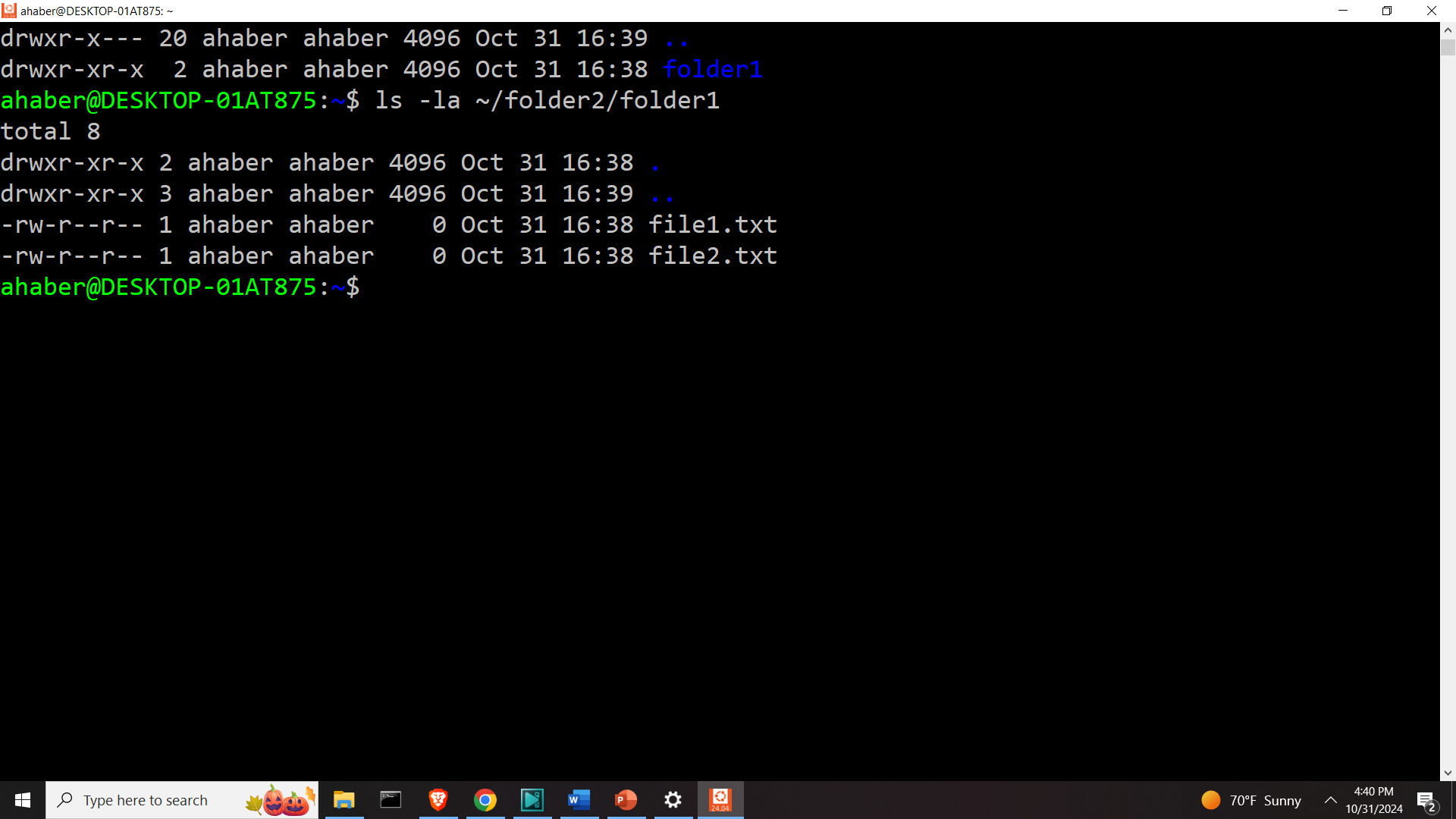
Next, let us create two sub folders inside of the folder2
mkdir ~/folder2/sub_folder2
mkdir ~/folder2/sub_folder3
Let us now move the content of the folder folder2 to the new folder folder3
mkdir ~/folder3
mv ~/folder2/* folder3
Let us list the content
ls -la ~/folder2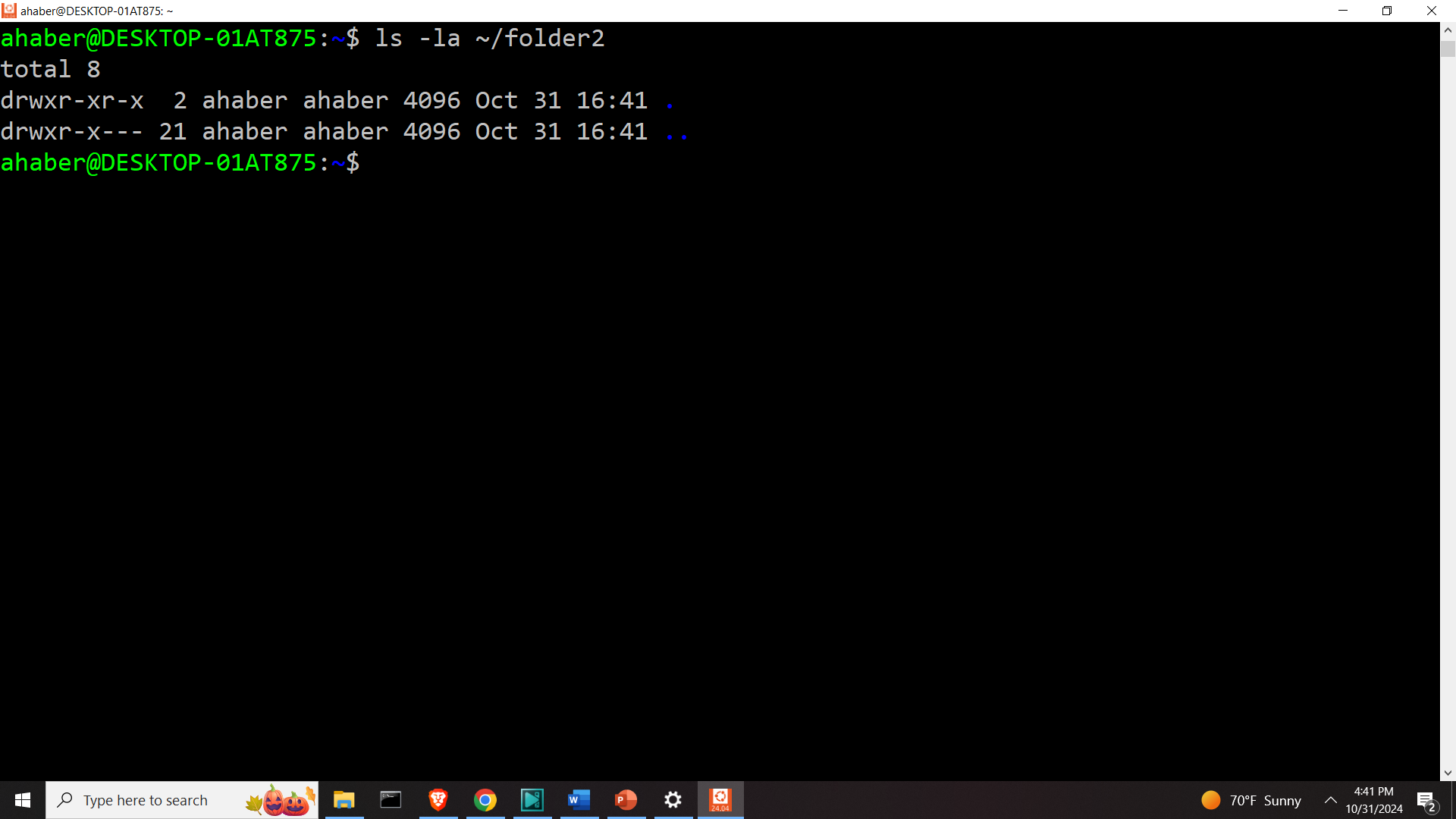
ls -la ~/folder3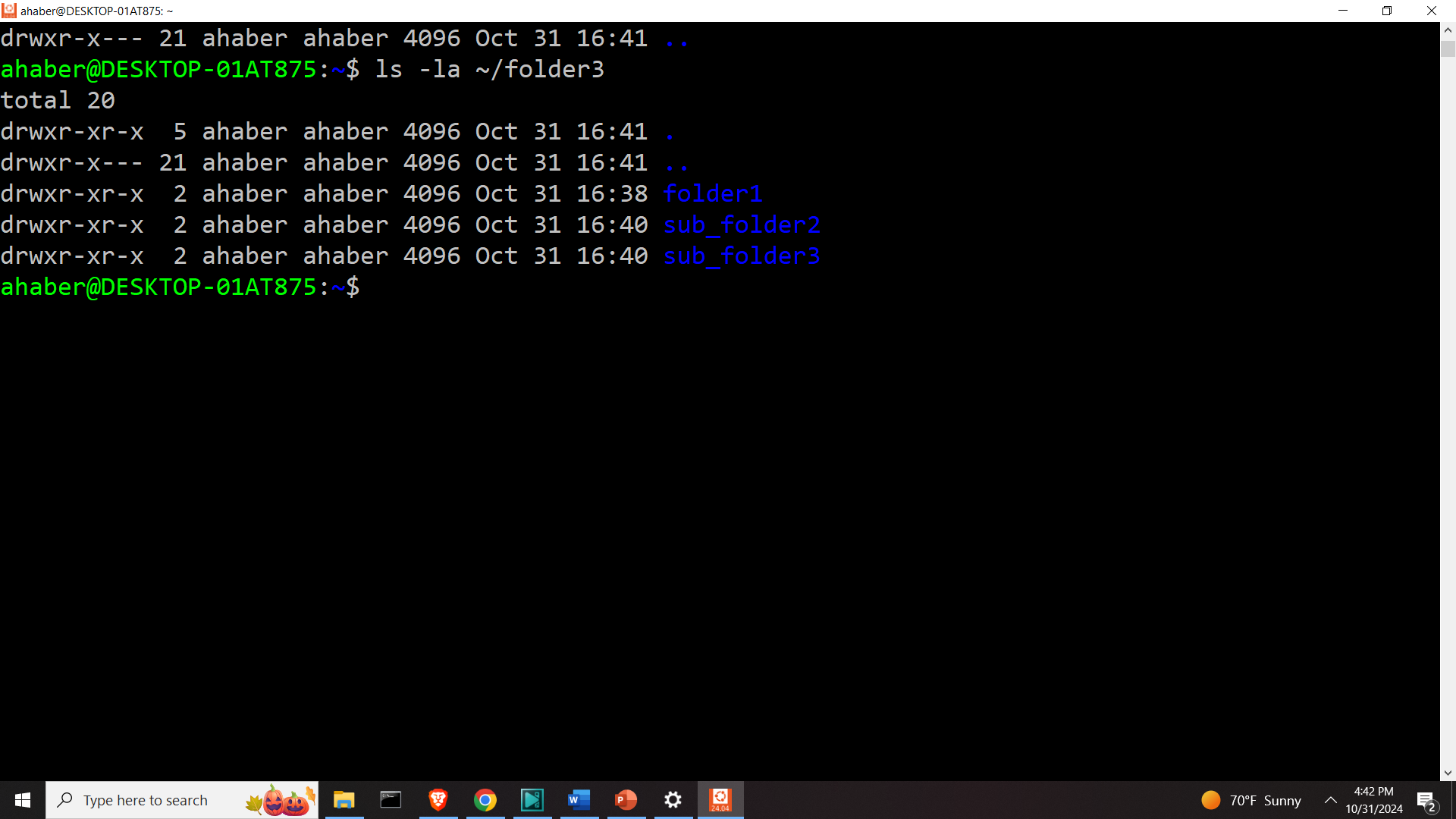
Let us erase the existing folders
cd ~
rm -rv ~/folder2
rm -rv ~/folder3
To copy the files and folders, we use the command cp. This command is similar to the move command mv. Let us explain how to use this command. Let us create a new folder
mkdir ~/dir5
mkdir ~/dir6
Create files in the folder ~/dir5
touch ~/dir5/file1.txt ~/dir5/file2.txt ~/dir5/file3.txtLet us copy the file
cp ~/dir5/file1.txt ~/dir6Let us confirm
ls -la ~/dir5
ls -la ~/dir6
Next, let us learn how to copy the folder. To do that, we need to use the option -r
cp -r ~/dir5 ~/dir6Finally, let us clean up everything:
cd ~
rm -r ~/dir5
rm -r ~/dir6