Gnuplot is a powerful command line tool for creating interactive scientific and professional looking plots. It can be used on Linux and Windows machines. You just need a command line to run Gnuplot. It was originally created by scientists to help scientists and students visualize different functions interactively. However, since then, gnuplot has been used outside the scientific community. In this tutorial, we explain how to install and use gnuplot on Windows. We will help you to get started with gnuplot and to generate your first graphs. We also explain how to run gnuplot script files and how to save graphs. The YouTube tutorial is given below.
How to Install and Use Gnuplot
To install gnuplot go to the official gnuplot website:
http://www.gnuplot.info/
and download the installation file by clicking on Release in the middle of the page. That link will lead you to the sourceforge website from where you can download the installation file. Run the installation file, and while installing the gnuplot tool make sure that the option to add gnuplot to the system path is selected.
After that to start gnuplot, open a windows command prompt and type
gnuplotIf everything is OK and gnuplot is in the system path you will see the screen shown below.
After running gnuplot, you will be in the gnuplot terminal from where you can execute the gnuplot commands. To generate the first graph, type this
plot sin(x)The result is given below
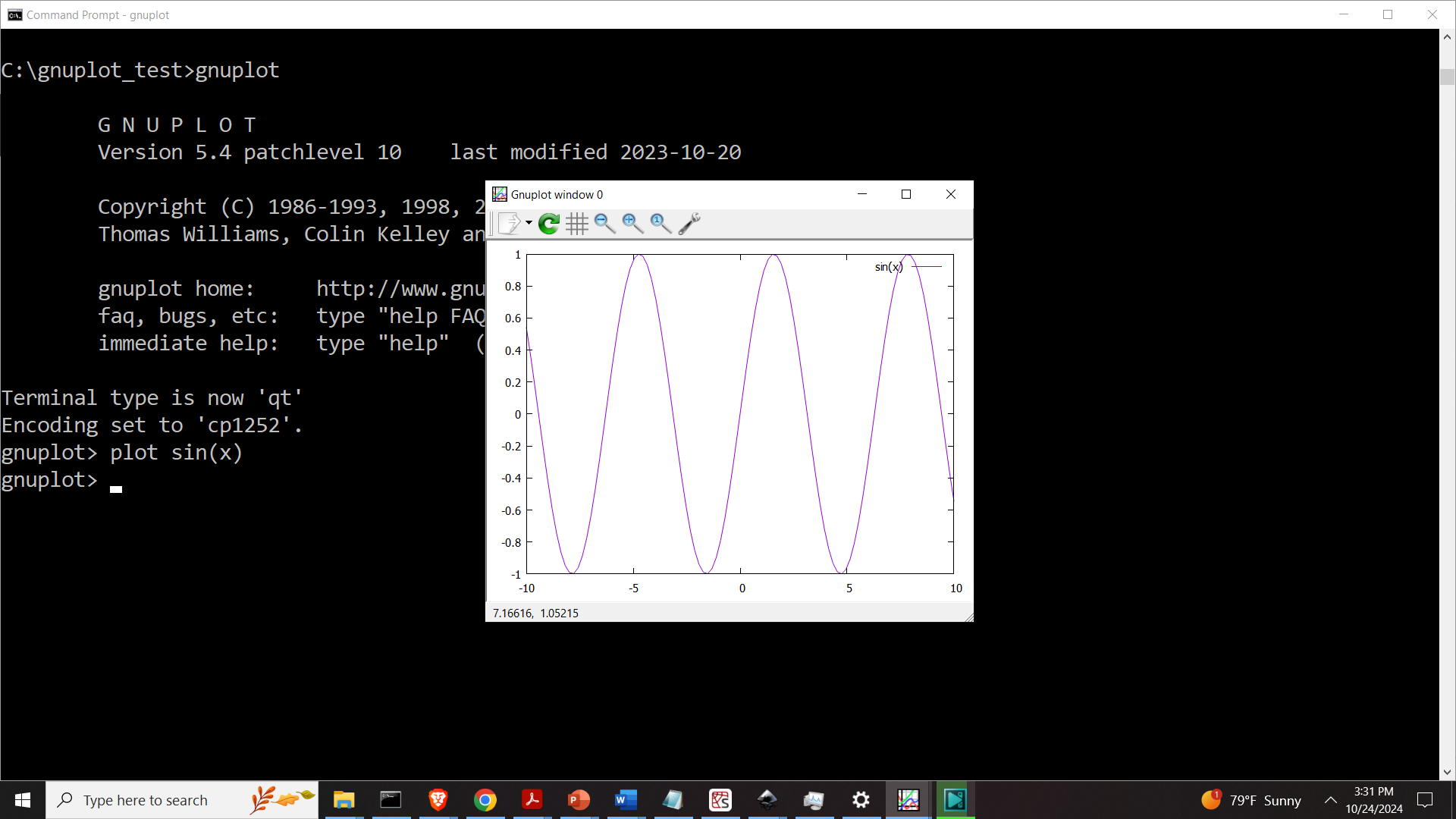
This will create an interactive plot and it will plot a sin function. To specify the x range of the function in gnuplot, type this
plot [-pi:pi] sin(x)where in the square brackets plot [-pi:pi] we set the plotting range. Note that this notation is very similar to the MATLAB or Python notation. We can change the plotting terminal, by first listing all styles
set terminaland then by selecting the plotting terminal. The two most popular ones in my opinion are windows and qt. We can switch between them like this. For windows, type this
set terminal windowsFor qt, type this
set terminal qtYou will see the effect of these commands after you generate a plot. To do that, after these commands, type this
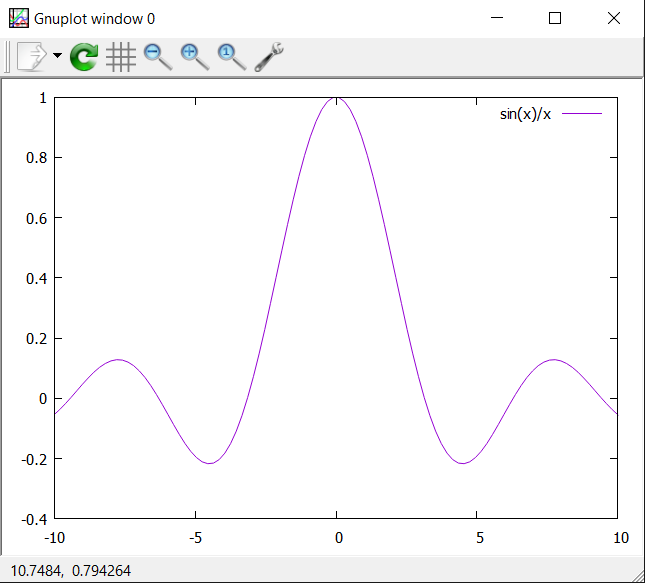
plot sin(x)/xto plot the sin(x)/x function. In my opinion, qt is nicer. As we will see later on, the command “set terminal” or the equivalent form “set term” can be used to redirect the plot to a file. The plot is shown below.
To specify both x and y axis ranges, type this
plot [-4*pi:4*pi] [-0.5:0.5] sin(x)To just specify the y range, you need to type this
plot [] [-0.5:0.5] sin(x)To plot two functions on the same graph, type this
plot sin(x)/x, sin(x)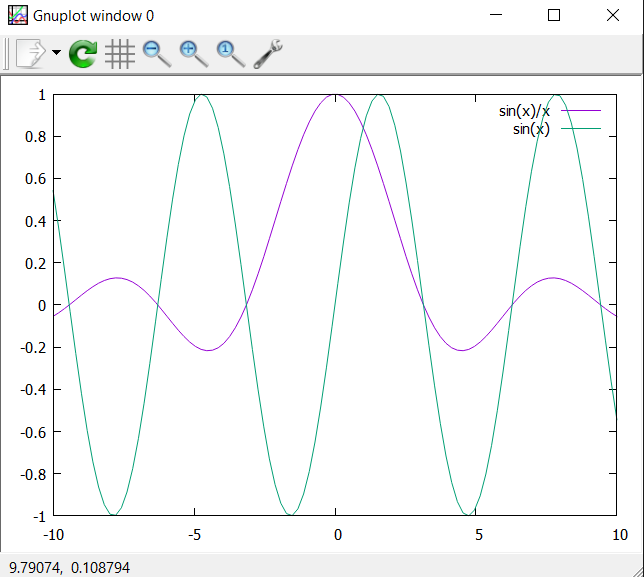
Two functions are separated by commas. To plot the functions with ranges, you need to type this
plot [-2*pi,2*pi] sin(x)/x, sin(x)Next, we need to explain how to use grid in gnuplot. Close all the graphs, and start defining the grid. First, let us define the grid resolution in the x and y directions:
set mxtics 5
set mytics 5
set grid mxtics mytics
plot cos(x)
To reset the grid, just type this
unset grid
replot
To generate a 3D plot
reset
splot 3*x**2+2*y**2
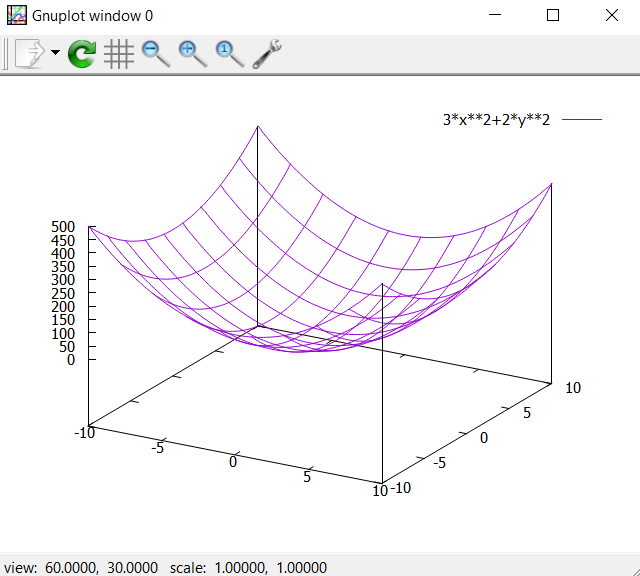
However, this plot might not look good. To improve the plot, we need to set the style
set hidden3d
splot 3*x**2+2*y**2
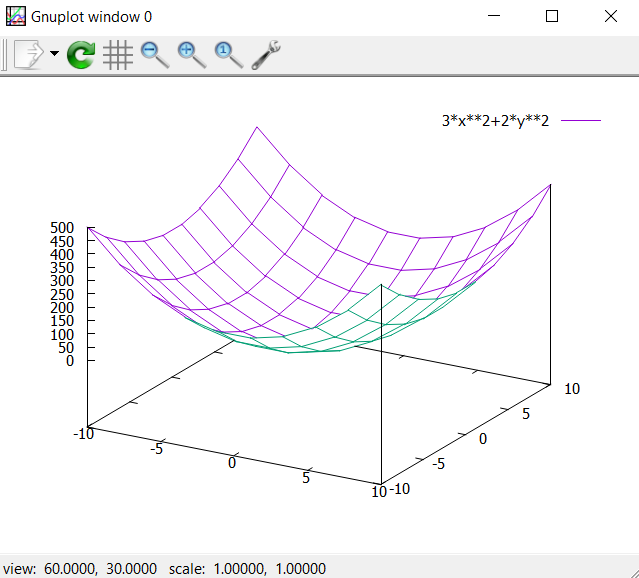
Even a nicer 3D plot can be obtained like this
set pm3d
splot 3*x**2+2*y**2
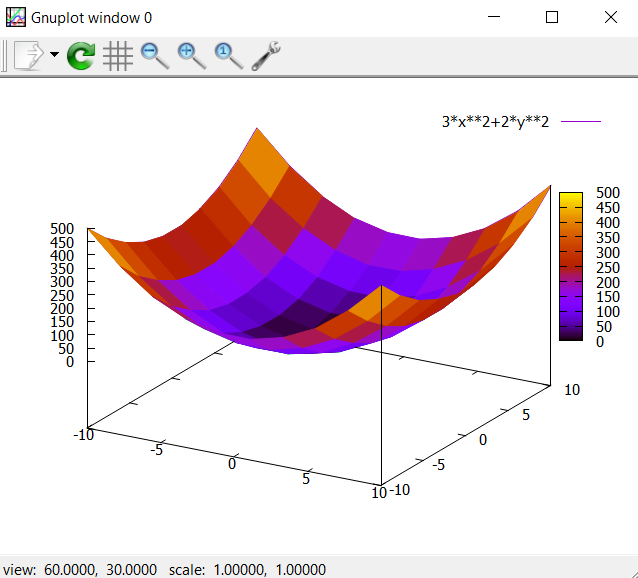
Let us set some limits
set pm3d
splot [-20:20] [-20:20] 3*x**2+2*y**2
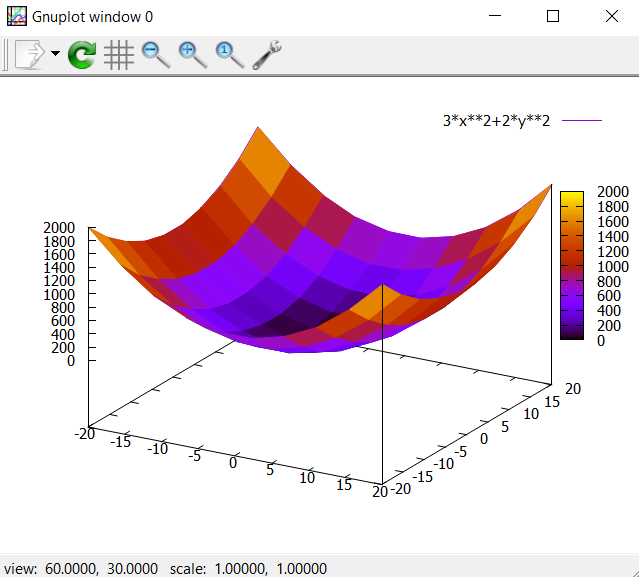
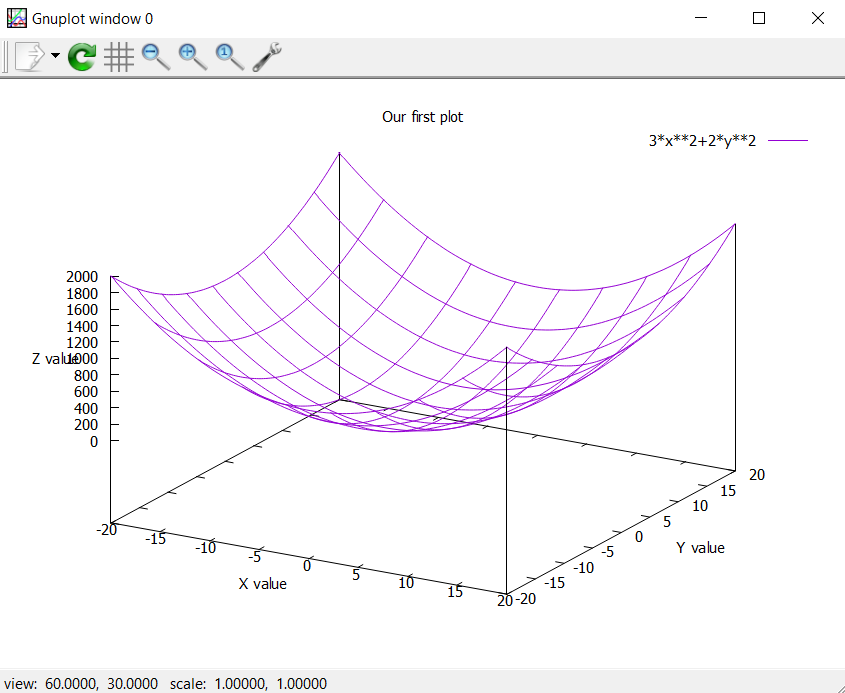
Let us learn how to set the x,y,z axis labels and to add the title
reset
set title "Our first plot"
set xlabel “X value”
set ylabel “Y value”
set zlabel “Z value”
splot [-20:20] [-20:20] 3*x**2+2*y**2
Save all the commands in a file
save ‘commands.plt’Here is how we save the plot to a png file
set term png size 600,600
set output "printme.png" (output to any filename.png you want)
replot
The file will be stored in the folder from which gnuplot is started.
Here, we have to set back the terminal to be a local window terminal
set term qt Finally, we explain how to run a gnuplot from a script since it is tedious to manually type commands in an interactive console. To exit the gnuplot terminal, type
exit Next, open a new file, and type this
# this is a comment in GNU plot
reset
plot [-5:5] sin(x)/x
set xlabel "time"
set ylabel "position"
Save this file as “test.plt”, and then in the command prompt type this:
gnuplot -p test.pltHere, we run gnuplot with the option -p. This option means that the gnuplot plot will not be closed after the gnuplot is executed.